Topics Covered in this Section
21.2 How is this Unit Organized?
21.4 Factors Affecting Boa Production
21.5 Some specific considerations of these factors applied to Boa Production in Captivity
21.6 An approach at developing an Intensive Animal Production System for the Boa
[I] The Objectives of the Production System or Model
III] The Physiological States for the Production Flow
[IV] Performance Coefficients or Growth Parameters
[VI] Animal Specific Needs as influenced by the Factors affecting animal Production Needs
[VII] Animal Behavior and Sociology
[VIII] Design of the Physical Environment Required
[IX] Management Routines Required
[XI] Output Expectations of the Model/Production Process Flow
AGLS 6502 Lecture 21 - Intensification of Boa Constrictor Production
1. to be able to describe the animal production factors affecting the Boa constrictor constrictor (Macajuel);
2. to understand the animal production coefficients and parameters for the Red- Tailed Boa and to see how this would relate to production of this species in captivity;
3. to become familiar with an approach to the intensification of Boa production and
4. to learn more about snakes in general.
21.2 How is this Unit Organized?
In this section / unit we would first attempt to gain a background understanding of the living and production needs of the Boa constrictor and snakes in general. Then we would attempt to simulate a commercial boid production system.
The Boa constrictor constrictor [ Macajuel] commonly grows to 2 to 3 m in length. The record length in the world is 4.2m but such large specimins are uncommon ( Freiberg, 1982). The colour of the snake is variable which may consist of a number of chocolate coloured saddles, fairly evenly spaced over a background colour of tan to grey. These saddles become a brick red colour on the tail and are outlined with black.
It has been reported by Freiberg (1982) that this species may produce from 30 to 50 neonates ranging in sizes from 40 to 50 cms (Mehrtens, 1987), they could be as long as 60cm (Ross,1990). The gestation period ranges from 4 to 6 months (Ross, 1990) and the young are born during the period May to September (Stafford, 1986).
21.4 Factors Affecting Boa Production
Environmental:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Surfaces
- Water
Nutritional:
Need Live/ warm feed [ Carnivorous ]
Breeding and Reproduction:
Gestation Length Variable
Copulation is a social activity
Diseases:
Be careful of Salmonella infection when working with snakes!!
21.5 Some specific considerations of these factors applied to Boa Production in Captivity
21.6 An approach at developing an Intensive Animal Production System for the Boa
Considerations for Species Production Modeling
The Species : Boa constrictor constrictor, Red Tailed Boa- Macajuel [ Trinidad, Guyana, Surinam ]
[I] The Objectives of the Production System or Model
(i) To develop a breeding colony of red tailed boas to get them to breed in captivity.
(ii) To grow out the captive born animals to maturity to be used as breeding stock.
(iii) To produce and sell juveniles to the pet trade.
(iv) To produce animal for release into the wild.
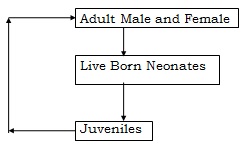
[III] The Physiological States for the Production Flow
- Adult Non-Breeding Male
- Adult Non Breeding Female
- Neonates
- Juveniles
- Breeding Males
- Breeding Females
- Pregnant [ gravid ] Females
[IV] Performance Coefficients or Growth Parameters
Growth will vary depending on sub-species, population characteristics, individual characteristics, temperature at which maintained and feeding regimes.
| Age | Parameter |
Newborn |
Length 14-22 ins |
Juvenile- 6 months |
Length ins |
12 months |
Length 3 to 5 feet [ 36 to 60 ins ] |
18 months |
Length ins |
24 months [ 2 years ] |
Length 4.5 to 7 feet [ 54 to 84 ins ] |
Note:
The relative growth rate of most boas significantly decreases after 24 months. Typically after 24 months the relative rate will decrease to 10-20% (in contrast to 100 to 300% during the first year ) and would continue to decrease as the animals becomes older. As a general rule Boa constrictor imperator from Colombia is the fastest growing of the Boas.
Adult-
3 years Length 4 to 6 feet [ 48-72 ins ]
Weight lb. [ kgs ]
5 years Length feet [ ins ]
Weight lb. [ kgs ]
Longevity:
Up to 20 years; but the record is 40 years, 3 months, 14 days at the Philadelphia Zoological Gardens.
Breeding Season:
Environmental Requirements for Breeding:
Male: Female Ratio for breeding:
Ratio for breeding is 3: 1
Length of Gestation:
The gestation length of Boas in captivity depends on: -
The Gestation length can range from 4 to 10 months.
Number of Neonates / Gravid Female: 11 to 60
[VI] Animal Specific Needs as influenced by the Factors Affecting Animal Production Needs
- Mature breeding grounds
- Neonates
- Juveniles
- Mature non breeding grounds
- Quarantine facility
- Sick animals facility
- Live Feed Production Facility
b. Nutrition and Feeding
Live warm prey required:
- Animals are carnivorous
- Live Mice, rats or rabbits [depending on body size] required once per week.
c. Health and Disease Control
Major diseases affecting Boas
- Ticks
- Mites
- Internal Parasites
- Stomatitis/ Mouthrot
- Skin Blister Diseaes
- Shedding Problems
- Respiratory Disorders
- Gastrointeritis
- Star Gazing Disease
[VII] Animal Behavior and Sociology
Remember that snakes can be very unpredictable so do not take any unnecessary chances!!
[VIII] Design of the Physical Environment Required for the following
- Mature breeding grounds [ Humid Tropical Jungle Type Environment ]
- Neonates
- Juveniles
- Mature non breeding grounds
- Quarantine facility
- Sick animals facility
- Live Feed Production Facility
[IX] Management Routines Required
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Seasonally
-Annually
[XI] Output Expectations of the Model/Production Process Flow
Breeding Stock:
50 Adult Females + 150 Adult Males
Live Juveniles/ Female / Year :
Replacement Breeders Needed/ year:
Marketable Juveniles/ Year:
Neonates / Female / Year:
Mortality:
Breeding Stock:
Neonates-
Juveniles-
Helpful Links, Photos, Videos and Multimedia